Anesthesiology News
Patients who underwent total knee replacement and used a smartphone app (PainCoach) at home after surgery consistently reduced opioid painkiller use and improved pain control, according to new research presented at the 2019 Euroanaesthesia Congress in Vienna.
The more the study participants used the app, the more likely they were to lower pain scores and decrease their use of opioids.
“These are important findings given the current demands on the health care system and the growing misuse of prescription painkillers worldwide,” said author Amar Sheombar, MD, from Kliniek ViaSana, in Mill, the Netherlands. “Few clinically tested mobile apps exist with clear measurable goals to guide patients in pain control and opiate use at home after surgery.”
To investigate the effect of the PainCoach app on pain and opiate use, Dutch researchers randomly assigned 71 patients aged 56 to 70 years undergoing total knee arthroplasty to the app and usual care (38 patients) or usual care alone (33) in the first two weeks at home after surgery.
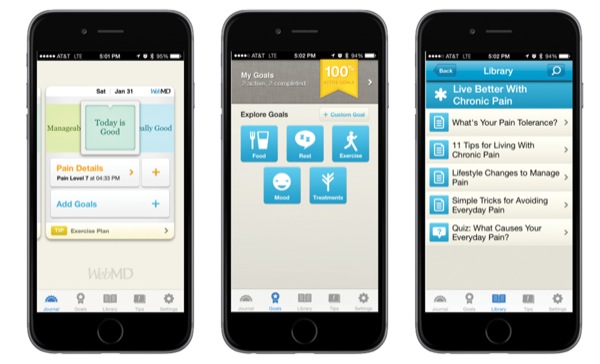
The mobile app allowed patients to input their pain level (no pain, bearable pain, unbearable pain or untenable pain), and based on this information and the amount of days after surgery, the app offered advice on drug pain relief use and exercises or rest.
Questionnaires were used to establish opiate use (oxycodone) and pain levels at rest, during activity and at night, as well as other pain drug use, experiences with exercises, pain acceptance, function and quality of life. Participants completed questionnaires preoperatively, daily during the first two weeks, and after one month.
The amount of app use was also recorded, with active use defined as at least 12 uses of the app over two weeks. During the study, the average visual analog scale pain score was 23 (the scale is 0-100 where 100 represents the highest pain), and average opiate use across the group was less than half of one 5-mg oxycodone tablet per day.
Compared with the control group, users of the PainCoach app used 23% less opiates and 15% more paracetamol in the first two weeks after surgery.
Regular use of the app led to further reduction in opiate use and improved pain control during activity and at night. Regular app users (19 patients) reported four times faster reduction in pain during activity, six times faster reduction in pain at night, and 44% less opiate and 76% less gabapentin use (taken to relieve nerve pain) compared with controls. Opiate use was substituted by 21% more paracetamol use in regular app users.
“Knowing that 80% of interactive advice is remembered may explain why regular use of the PainCoach app contributes to lower pain scores and reduced opiate use,” Dr. Sheombar said. “Digital innovations like smartphone health care apps must empower patients and deliver patient-centric care. Three-quarters of the study patients found our app valuable and wanted to use it for real-time feedback and support. In the current study population, opiate use was already low. The app might have a much stronger effect in patient populations where preoperative opiate use is much higher.”
Misuse of prescription painkillers is a growing public health problem worldwide. In the United States, an estimated 18 million Americans misused prescription painkillers at least once in the past year, and overdose deaths involving prescription opioid pain relievers were five times higher in 2016 than in 1999.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.